‘Funding’ refers to the money required to start and run a business. It is a financial investment in a company for product development, manufacturing, expansion, sales and marketing, office spaces, and inventory. Many startups choose to not raise funding from third parties and are funded by their founders only (to prevent debts and equity dilution). However, most startups do raise funding, especially as they grow larger and scale their operations.
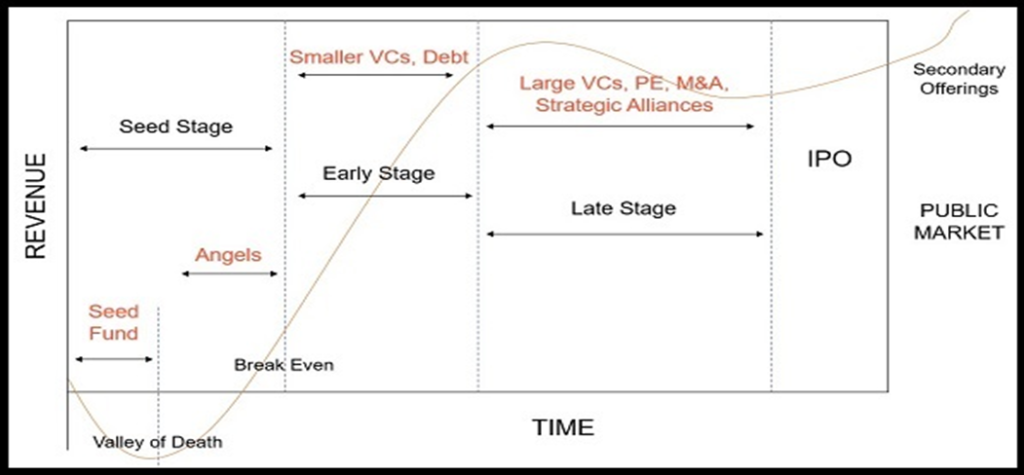
- Ideation/Pre-Seed Stage:
This is the stage where you, the entrepreneur, has an idea and are working on bringing it to life. At this stage, the amount of funds needed is usually small.
Given the fact that you are at such an initial stage in the startup lifecycle, there are very limited and mostly informal channels available for raising funds. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
•Bootstrapping/Self-financing: Bootstrapping a startup means growing your business with little or no venture capital or outside investment. It means relying on your own savings and revenue to operate and expand. This is the first recourse for most entrepreneurs as there is no pressure to pay back the funds or dilute control of your startup.
•Friends and Family: This is also a commonly utilized channel of funding by entrepreneurs still in the early stages. The major benefit of this source of investment is that there is an inherent level of trust between the entrepreneurs and the investors
•Business Plan/Pitching Events: This is the prize money/grants/financial benefits that is provided by institutes or organizations that conduct business plan competitions and challenges. Even though the quantum of money is not generally large, it is usually enough at idea stage. What makes the difference at these events is having a good business plan.
2. Validation/Seed Stage:
This is the stage where your startup has a prototype ready and you need to validate the potential demand for your startup’s product/service. This is called conducting a ‘Proof of Concept (PoC)’, after which comes the big market launch. To do this, the startup will need to conduct field trials, test the product on a few potential customers, onboard mentors, and build a formal team. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
•Incubators: Incubators are organizations set-up with the specific goal of assisting entrepreneurs with building and launching their startups. Not only do incubators offer a lot of value-added services (office space, utilities, admin & legal assistance, etc.), they often also make grants/debt/equity investments
•Government Loan Schemes: The government has initiated a few loan schemes to provide collateral-free debt to aspiring entrepreneurs and help them gain access to low-cost capital. Some such schemes include CGTMSE, MUDRA, and Stand-up India.
•Angel Investors: Angel investors are individuals who invest their money into high potential startups in return for equity. Reach out to angel networks such as Indian Angel Network, Mumbai Angels, Lead Angels, Chennai Angels, etc. or relevant industrialists for this.
•Crowd funding: Crowdfunding refers to raising money from a large number of people who each contribute a relatively small amount. This is typically done via online crowdfunding platforms.
3. Early Traction/Series A Stage:
This is the stage where your startup’s products or services have been launched in the market. Key performance indicators such as customer base, revenue, app downloads, etc. become important at this stage. Funds are raised at this stage to further grow user base, product offerings, expand to new geographies, etc. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
•Venture Capital Funds: Venture capital (VC) funds are professionally managed investment funds that invest exclusively in high-growth startups. Each VC fund has its own investment thesis – preferred sectors, stage of startup, and funding amount – which should align with your startup. VCs take startup equity in return for their investments and actively engage in mentorship of their investee startups.
•Banks/NBFCs: Formal debt can be raised from banks and NBFCs at this stage as the startup can show market traction and revenue to validate their ability to finance interest payment obligations. This is especially applicable for working capital. Some entrepreneurs might prefer debt over equity as they debt funding does not dilute equity stake
•Venture Debt Funds: Venture Debt funds are private investment funds that invest money in startups primarily in the form of debt. Debt funds typically invest along with an angel or VC round.
•TReDs: To decrease the financing concerns faced by MSMEs in India, RBI introduced the concept of TReDS in 2014, an institutional mechanism for financing trade receivables on a secure digital platform. Trade Receivable Exchanges such as M1xchange, standardizes the process of funding MSMEs via Invoice Discounting. TReDS addresses the gaps in MSME industry as enterprises face challenges in getting their payments on time, thus creating working capital discrepancies. TReDS is a timely and effective solution to drive the MSME sector to the next phase of Indian economy.
4. Scaling/Series B & Above Stage
At this stage, the startup is experiencing fast rate of market growth and increasing revenues. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
•Venture Capital Funds: VC funds with larger ticket size in their investment thesis provide funding for late stage startups. It is recommended to approach these funds only after the startup has generated significant market traction. A pool of VCs may come together and fund a startup as well.
•Private Equity/Investment Firms: Private equity/Investment firms generally do not fund startups however, lately some private equity and investment firms have been providing funds for fast-growing late-stage startups who have maintained a consistent growth record.
5. Initial Public Offering:
Initial Public Offer (IPO) refers to the event where a startup lists on stock market for the first time. Since the public listing process is elaborate and replete with statutory formalities, it is generally undertaken by startups with an impressive track record of profits and who are growing at a steady pace. One of the benefits of an IPO is that a public listing at times can increase the credibility of the startup and be a good exit opportunity for stakeholders.
Any Angel investor, VC, or PE fund may buy out investors of a previous round to get their equity share as well. Also, there are various State Policies also which help the startups in various phases of funding or give them incentives and allowances to help them grow.
Source: startupindia.gov.in